Section:
New Results
Multi-subject dictionary learning (MSDL) to segment an atlas of brain spontaneous activity
Fluctuations in brain on-going activity can be used to reveal its
intrinsic functional organization. To mine this information, we give a
new hierarchical probabilistic model for brain activity patterns that
does not require an experimental design to be specified. We estimate
this model in the dictionary learning framework, learning
simultaneously latent spatial maps and the corresponding brain
activity time-series. Unlike previous dictionary learning frameworks,
we introduce an explicit difference between subject-level spatial maps
and their corresponding population-level maps, forming an atlas. We
give a novel algorithm using convex optimization techniques to solve
efficiently this problem with non-smooth penalties well-suited to
image denoising. We show on simulated data that it can recover
population-level maps as well as subject specificities. On
resting-state fMRI data, we extract the first atlas of spontaneous
brain activity and show how it defines a subject-specific functional
parcellation of the brain in localized regions.
See also [25] and Fif 4 .
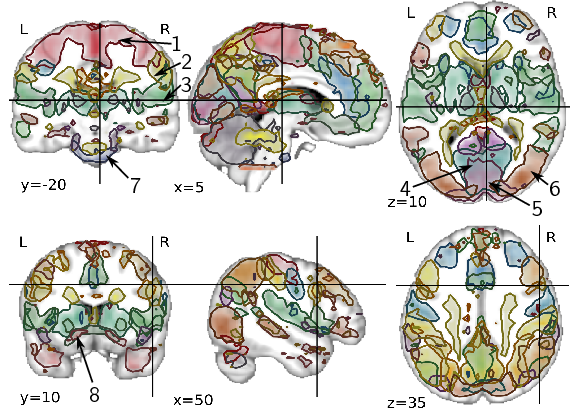
Figure
4. Outlines at 33% of all dictionary elements estimated by
MSDL for 2 different set of cutting
planes.
The motor system is divided in (1) dorsal, (2)
lateral, and (3) ventral regions. Similarly, the visual
system is divided in (4) a primary region centered on the
Calcarine sulcus, overlapping with (5) a region centered on
the striate cortex, and (6) extrastriate regions.
(7), (8): fine details of the vascular system
segmented in several maps. |